.
The process begins with starting stock, usually a cast ingot (or a "cogged" billet which has already been forged from a cast ingot), which is heated to its plastic deformation temperature, then upset or "kneaded" between dies to the desired shape and size.
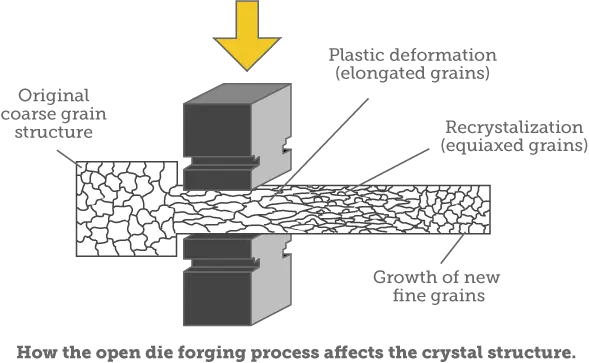
During this hot forging process, the cast, coarse grain structure is broken up and replaced by finer grains. Shrinkage and gas porosity inherent in the cast metal are consolidated through the reduction of the ingot, achieving sound centers and structural integrity. Mechanical properties are therefore improved through reduction of cast structure, voids and segregation. Forging also provides means for aligning the grain flow to best obtain desired directional strengths. Secondary processing, such as heat treating, can also be used to further refine the part.
When steel is heated to forging temperature, it becomes ductile and malleable and be molded to a shape of our choice by applying pressure. With proper processing methods, steel forging allows a billet of steel to be shaped permanently without cracking, due to its plasticity.
Steel forging can be classified into three categories depending upon the forming temperature:
Forging can create a myriad of sizes and shapes with enhanced properties when compared to castings or assemblies.
