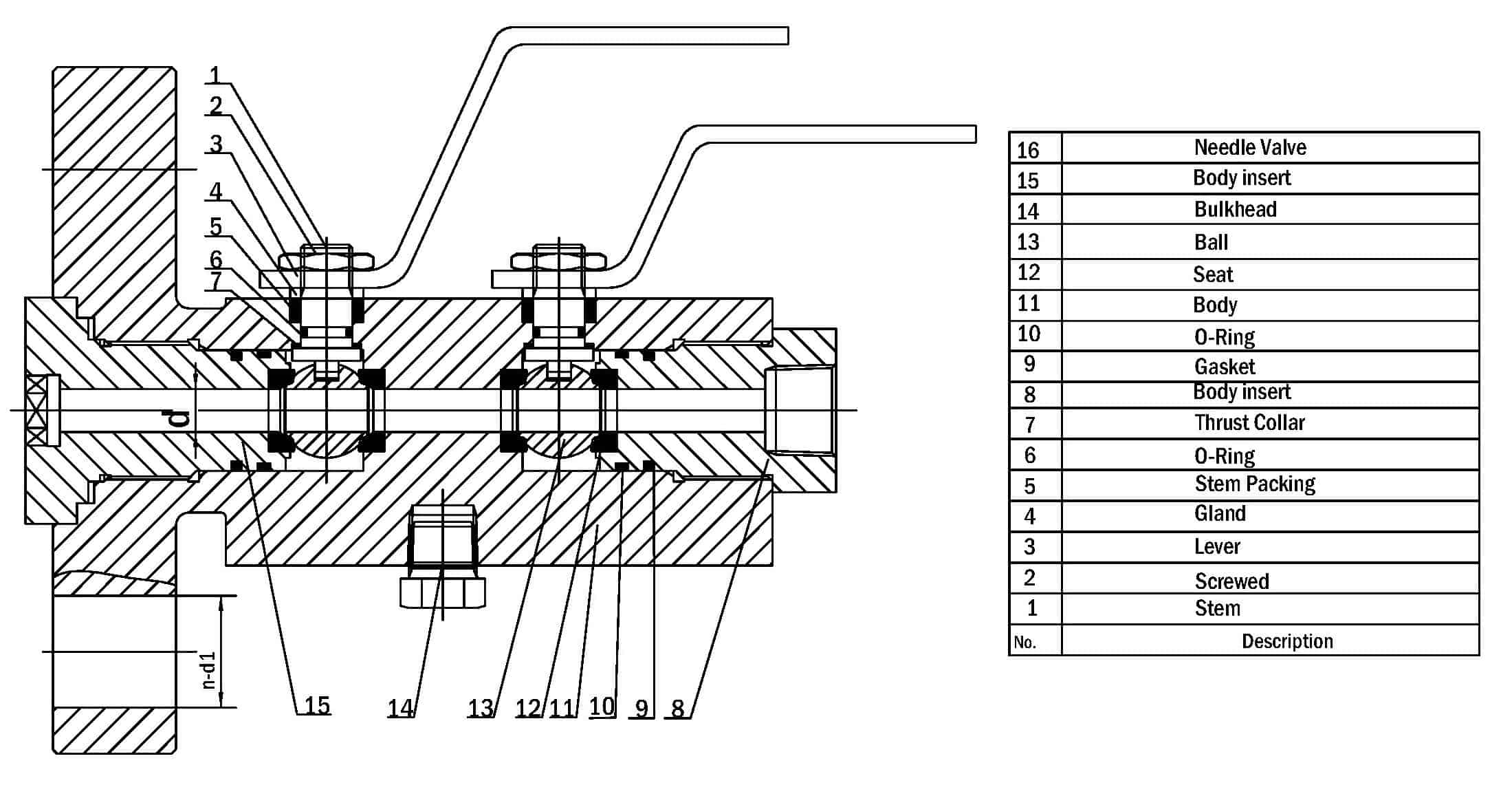
DIB ball valve provides a seal against pressure from a single source, with a means of venting/bleeding the cavity between the sealing surfaces.
DIB ball valve definition in API 6D:
Single ball valve with two seating surfaces, with two sealing surfaces, each of which, in the closed position, provides a seal against pressure from a single source, with a means of venting/bleeding the cavity between the sealing surfaces. This feature can be provided in one direction or in both directions
Two types of DIB ball valves:
DIB-1 Ball Valve: Double Piston Seat x Double Piston Seat
For the DIB Double Piston x Double Piston (DIB-1)configuration, over pressurization of cavity is external with a safety valve.
Upstream and downstream sealing; pressure energized; two seats are bidirectional sealing seats.
Advantage: Each seat can isolate the fluid from upstream and downstream, if one seat is damaged, the other seat still work to ensure the sealing performance.
DIB-1 Ball Valve

DIB-2 Ball Valve

DIB-2 Ball Valve: DPE Seat x Self Relieving Seat
For the DIB Self relieving x double piston (DIB-2) configuration, cavity over pressurization is internally controlled within the line.
Upstream and downstream sealing; pressure energized; one seat is bidirectional seat and one seat is unidirectional sealing seat.
For DIB-2 Ball Valve, the fluid can be relieved from one seat to downstream side.
Advantage: Self-relieving seat, no need to assembly the safety valve for pressure relieving.
Both DIB-1 & DIB-2 are for trunnion mounted ball valve structure.
The double block and bleed valve is abbreviated to DBB valve. It is made up of two ordinary ball valves linked by a common inlet end. The double block and bleed ball valve is a product intended to substitute several connections between conventional valves; as the name suggests, it is a double block and bleed ball valve. The distinction between this DBB valve and the conventional one is that it can effectively overcome leakage that happens during system operation, and it can be quickly closed and can discharge easily. This DBB ball valve is a modern form of valve that is commonly used on the market today.
What is a Double block and bleed Valve?
Two agencies officially describe Double block and bleed valve in different terms.
Double-block-and-bleed valve (DBB) is defined by API 6D as a “single valve with two seating surfaces that, in the closed position, provides a seal against pressure from both ends of the valve with a means of venting/bleeding the cavity between the seating surfaces.” When just one side is under pressure, this valve does not have positive double isolation, according to the 2008 note.
And OSHA defines DBB valve as “the closure of a line, duct, or pipe by closing and locking or tagging two inline valves and by opening and locking or tagging a drain or vent valve in the line between the two closed valves”.
Double block and bleed valve classification.
DBB valves are classified by their body structure into two main types:
Modular or Split Body Type DBB Valve – The main feature of this design is that it has two balls in one valve to ensure greater safety. A drain needle valve is located between the two balls on the Double Block & Bleed valve. This allows the valve to be drained and the pressure to be reset to zero. Instrumentation and piping all benefit from the modular form, three-piece body construction. Instrumentation valves range in size from 1 inch to 3 inches; piping valves range in size from 1 inch to 24 inches. API 3.000 to API 10.000 in all pressure class scores from 150 to 2500 lbs.
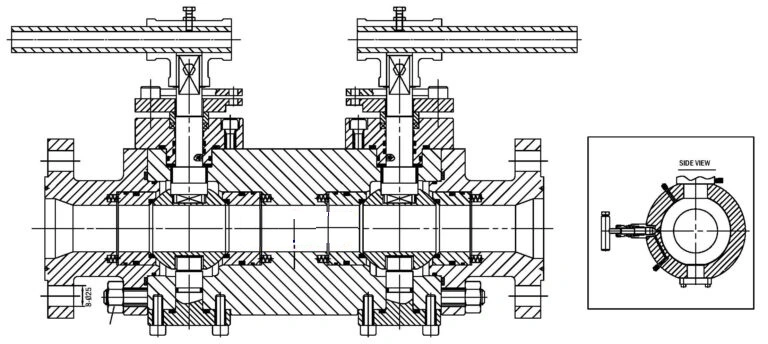
Integral DBB Valves – These valves are used in the instrumentation industry and come in a variety of designs to meet a variety of needs, including flange to flange, flange to the thread, injection, and sampling, and ball and needle types. A drain needle valve is located between the two balls on the Integral Double Block & Bleed valve. This allows the valve to be drained and the pressure to be reset to zero.
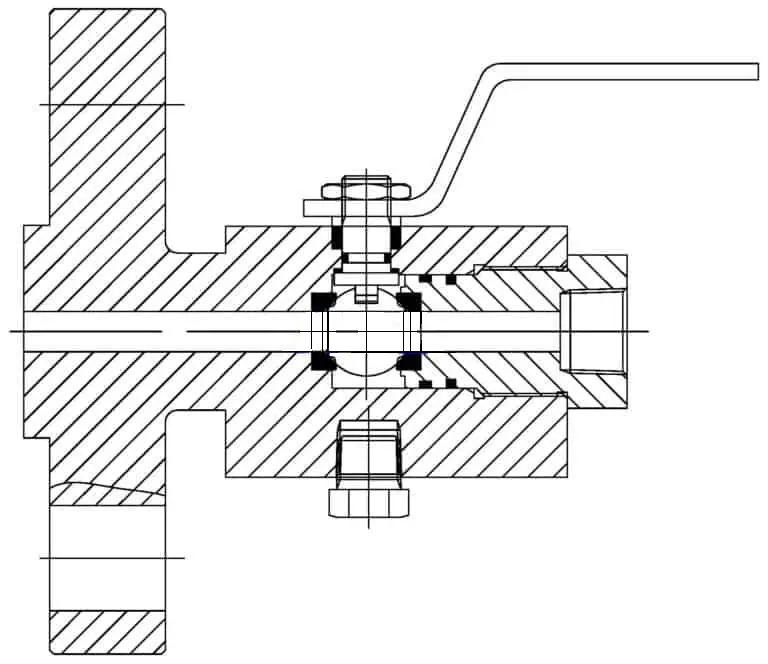
Features and Benefits of DBB Valve.
Double Block and Bleed valves have been developed to substitute the process of bolting the individual valves together to provide dual insulation.
This new model provides excellent savings in weight, space, and installation time, particularly for insulation in the instrument or instrument cage. These weight savings will amount to up to 60% and tests have shown that a time savings of 70% on installation is also possible. The biggest benefits must be seen, however, in reducing the leakage pathways into the environment, thus reducing the possibility of possible dangers.
Dual isolation is an essential requirement when maintenance is performed downstream of the first isolation valve. Cavity venting is given by either a ball or a globe vent valve such that the compressed pressure between the two isolation valves is vented safely.
These valves have also grown to incorporate the role of chemical injection and sampling points. In-built control valves are also incorporated into these valves.
Application of Double Block and Bleed Valve.
DBB valves are used where critical sealing is necessary to make sure no leakage occurs. Both valves can operate in various applications and industries, such as the Natural Gas industry, petrochemical, transmission and storage, industrial processes for natural gas, main-line and multi-purpose valves in liquid pipelines, and transmission lines of refined materials.
The demand for meters calibration is another application where the DBB valve is used. Each valve closed to the meter device must be tightly sealed. Even a minor leak causes errors in meter calibration and the inaccurate meter factor remains until the next proven procedure and large sums are required. Choosing the right DBB or DIB valve tested for API will help ensure the calibration is accurate almost every time.