Industrial valves have been around for more than a century. As applications become more specific and complicated, valves have evolved into nine major types to suit different requirements. These 9 types cover all industrial applications and services.
Valve categorization depends on several considerations. For this article, valves are categorized according to the functions. Some take only one while most have two, depending on the valve design.
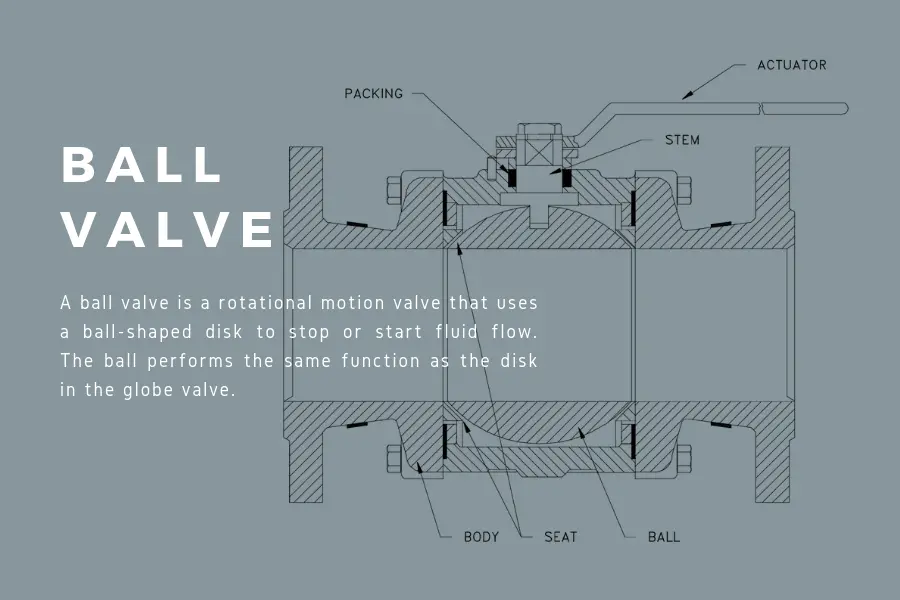
Ball valve is part of the quarter turn valve family. The distinct feature of a ball valve is its hollow ball-shaped disc that acts to stop or start media flow. The ball disc is one of the quickest valves because it only needs a quarter turn to open or close.
- ● Great shut on/off capability.
- ● Minimal leakage through wear & tear if properly used.
- ● Low maintenance cost.
- ● Minimal pressure drop.
- ● Time & labor effective to operate.
- ● Not suitable as control or throttling valve.
- ● Not suitable for thicker media as sedimentation could occur and damage the valve disc & seat.
- ● Surge pressure could occur due to rapid closing and opening.
Ball valves are suitable for fluid, gaseous and vapor applications that need bubble-tight shutting down. While primarily for low pressure uses, high pressure and high temperature applications apply to ball valves with metal seats.
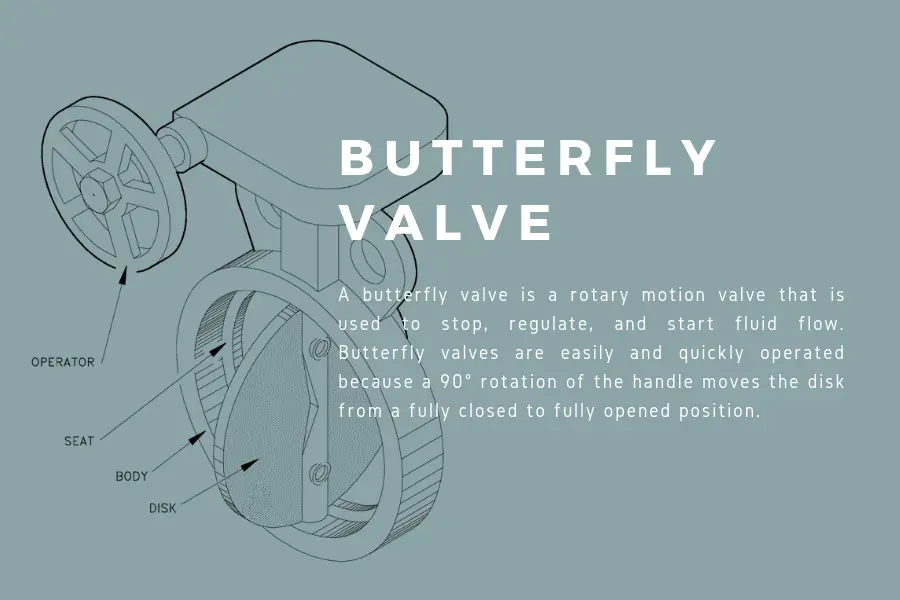
Butterfly valve is also part of the quarter turn valve family. What makes butterfly valve distinct from the other valves is the flat to a concave disc that attaches to the valve stem.
Positioned in the middle of the valve with the stem bored into it or attached at one side, the disc blocks media flow when the valve is closed. The stem adds support to the disc. This design allows butterfly valve to throttle when there is incremental opening of the valve.
- ● Compact design.
- ● Lightweight.
- ● Minimal pressure drop.
- ● Easy to install.
- ● Limited throttling capabilities.
- ● Strong pressure may affect disc movement.
Butterfly valves are often used in water and gas applications where there is a need to isolate or interrupt the flow of media. Butterfly valves are great for processes that use large diameter pipes. They are also suitable for slurries, cryogenics, and vacuum services.
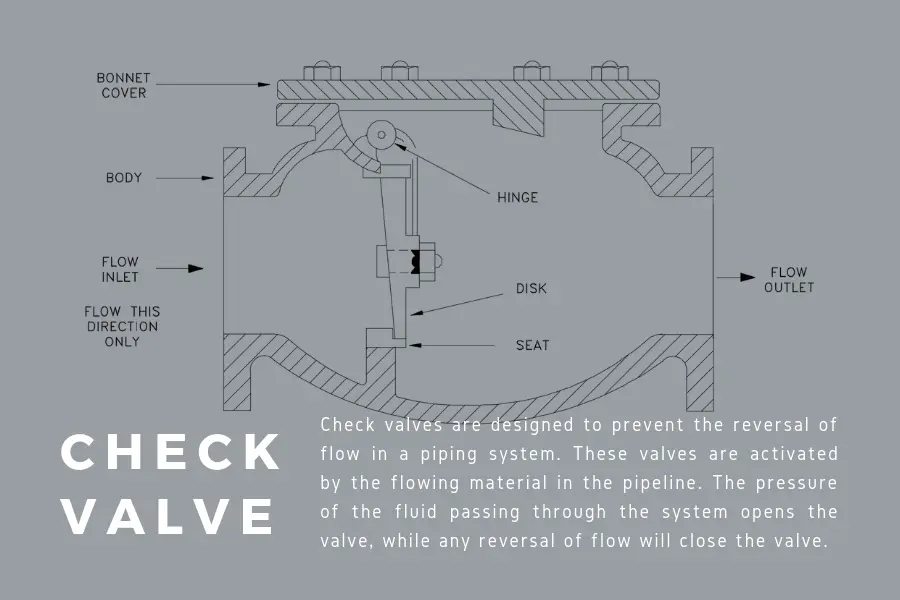
Check valve relies on internal pressure, instead of outside action, for opening and closing. Also known as non-return valve, prevention of backflow is the main function of a check valve.
- ● Simple design.
- ● No need for human intervention.
- ● Effectively prevent backflow.
- ● Can be used as a backup system.
- ● Not great for throttling.
- ● The disc may potentially get stuck in the open position.
Check valves are used in applications that need backflow prevention such as pumps and compressors. Feed pumps in steam boilers often use check valves. Chemical and power plants have a variety of processes that also utilize check valves. Check valves are also used when there is a combination of gases in one pipeline.
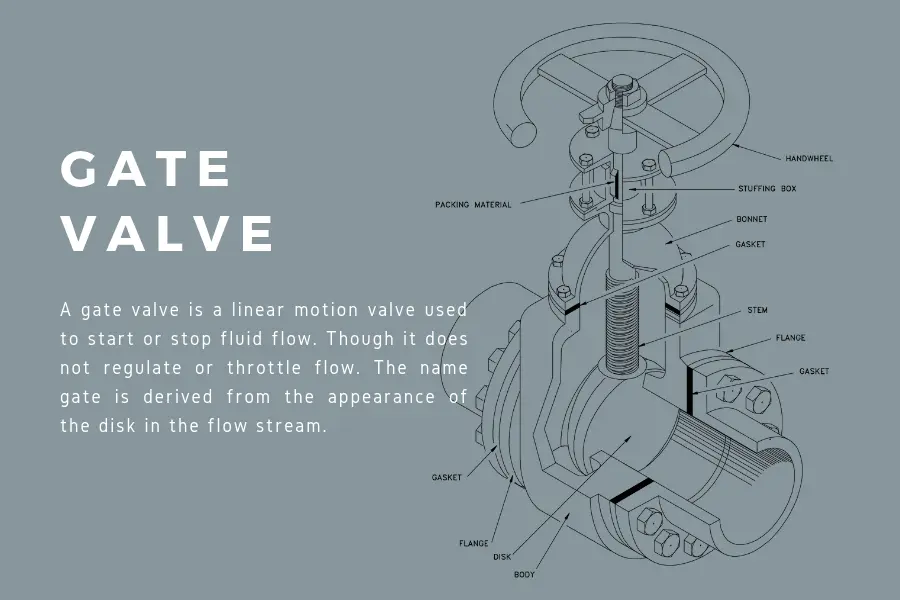
Gate valve is another member of shut off/on valve family. What makes this unique is its disc movement is linear. The disc is either gate or wedge-shaped, which has an effective shut-off and on mechanism. Gate valve is primarily suited for isolation.
While it is possible to use it as a throttling valve, this is not advisable as the disc may get damaged by media vibration. The surge of the media can damage the disc when gate valves are used half-closed in a throttling application.
- ● No media flow resistance since the gate does not obstruct the flow when fully opened.
- ● Can be used in bi-directional flows.
- ● Simple design.
- ● Suitable for pipes with large diameters.
- ● Not good throttlers since accurate control is not possible.
- ● Media flow intensity could damage the gate or disc when used for throttling.
Gate valves are great shut off/on valves for any application. They are suitable for wastewater applications and neutral liquids. Gases that range between -200C and 700C with a maximum 16 bar pressure can use gate valves. Knife gate valves are used for slurries and powder media.

Globe valve looks like a globe with a plug-type disc. It is part of the linear motion valve family. Aside from being a great turn off/on valve, globe valve also has great throttling capabilities.
Similar to gate valve, globe valve disc moves up unobstructedly to allow the flow of media. This is a great valve alternative for applications that do not require high-pressure drops.
- ● Better shutting mechanism than gate valve.
- ● Wear & tear is not an issue even for frequent use.
- ● Easy to repair as disassembly is easy.
- ● High-pressure loss could occur from obstructions of the media flow path
- ● Not great for high-pressure applications.
Globe valves perform well when the major concern is leakage. High point vents and low point drains use globe valves. Also, globe valves work when the pressure drop is not a concern. Regulated flow applications such as cooling water systems use globe valves.
Other applications for globe valves include feedwater systems, chemical feed systems, extraction drain systems and the likes.
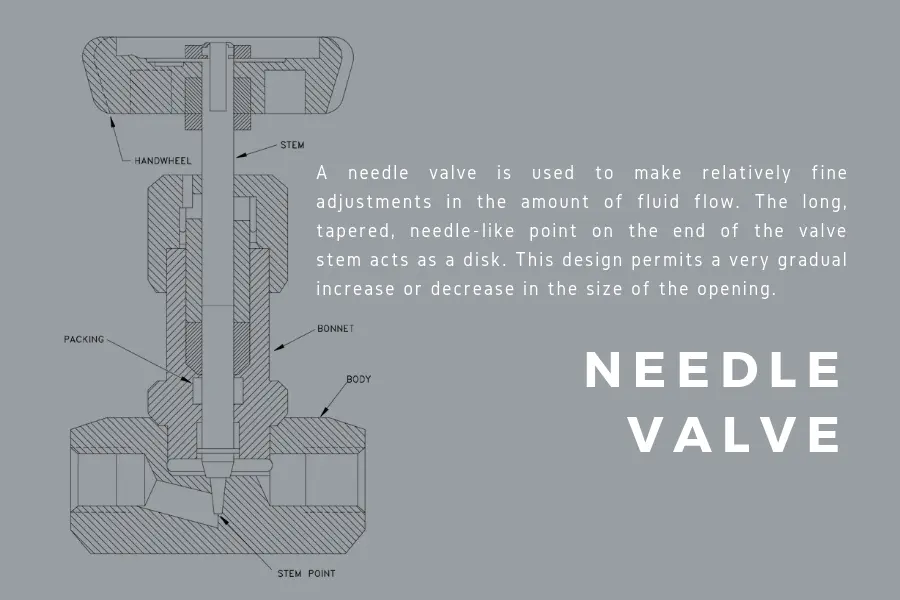
Needle valve gains its name from the needle-like shape of its disc. Its mechanism acts similarly to that of globe valve. Needle valve provides more precision and control in smaller piping systems. Still part of the quarter turn family, needle valve functions better in low flow rates.
- ● Effective in controlling fluid media.
- ● Ideal in vacuum services or any system that requires precision.
- ● Requires minimal mechanical force to seal the valve.
- ● Used only in more sophisticated shut-off applications.
- ● Requires quite a few turns to completely turn off and on.
Needle valves are used in instruments that need fuller control for fluid surge and more precision of fluid flow. Needle valves are more commonly used in calibration applications. They are also associated with distribution points in pipe systems, where needle valves are used as a regulator of media.
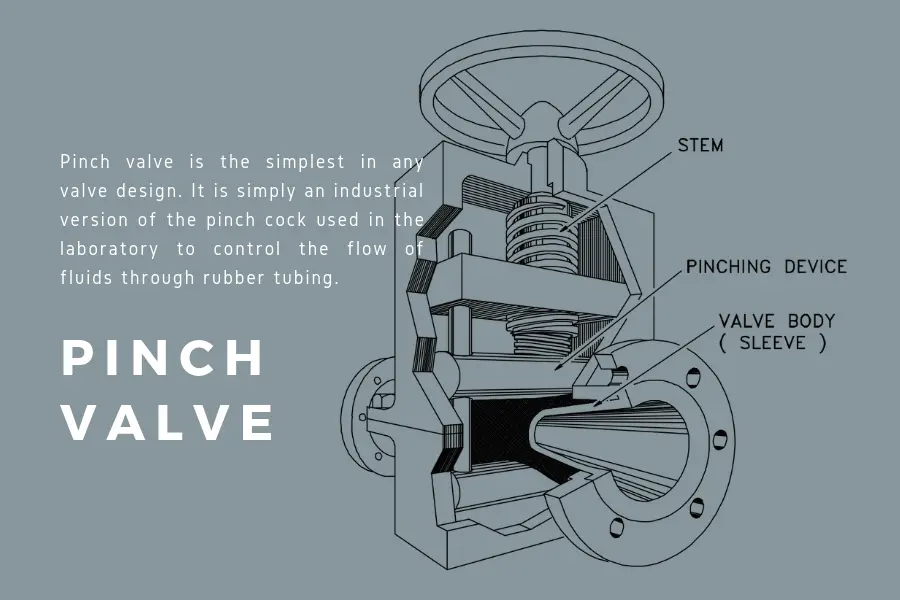
Also called the clamp valve, pinch valve is another valve for stop/start and throttling. Pinch valve belongs to the linear motion valve family. The linear motion allows unobstructed flow of media. The pinching mechanism of the pinch tube inside the valve acts to control the fluid flow.
- ● Simple design with no internal moving parts.
- ● Ideal for slurries and thicker, even corrosive media.
- ● Useful to prevent media contamination.
- ● Low maintenance cost.
- ● Not suitable for high-pressure applications.
- ● Not ideal to use for gas.
Pinch valves are mostly used for unrestricted fluid flow. They are most suitable for slurry applications. Pinch valves are great for applications that need complete isolation from valve parts as well as environmental contaminants.
Other applications that employ pinch valves include wastewater treatment, chemical processing, cement handling, among others.
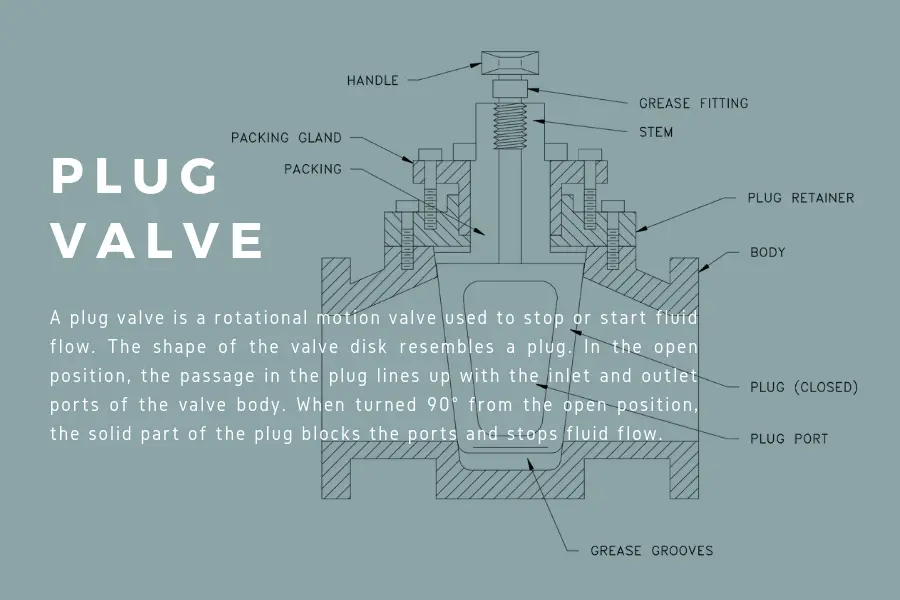
Plug valve belongs to the quarter turn valve family. The disc acts as a bubble tight shut-off and on plug or cylinder. Aptly named as the plug valve due to its tapered end. Its closing and opening mechanism is similar to that of a ball valve.
- ● Simple mechanism.
- ● Easy in-line maintenance.
- ● Low-pressure drop.
- ● Reliable and tight seal capability.
- ● Fast-acting to open or close as it only needs a quarter turn.
- ● The design allows high friction so it often needs an actuator to close or open the valve.
- ● Not suitable for throttling purposes.
- ● Needs power or automated actuator.
Plug valves are effective tight shut-off and on valve. There are many applications that use plug valves. These include gas pipelines, slurries, applications that contain high levels of debris, as well as high temperature and pressure applications.
These valves are great for sewage systems. Since there is no contact between the media and the internal valve parts, plug valves are also great for highly abrasive and corrosive media.
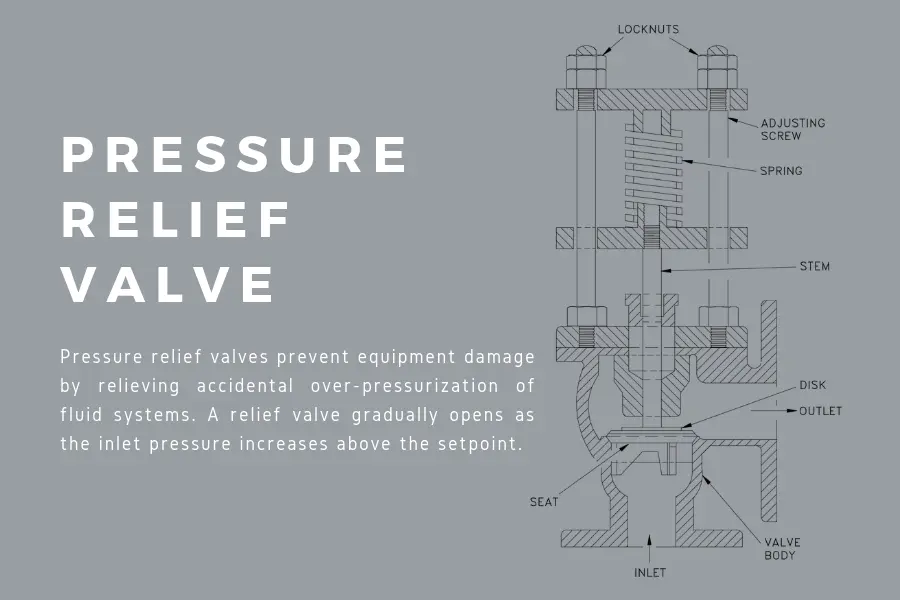
Pressure relief valve refers to a valve that releases or limits pressure from the pipelines to maintain the pressure balance and to avoid build-up. It is sometimes mistakenly called the pressure safety valve.
Its main purpose is to protect the equipment in an overpressured event, or to increase pressure when there is a drop. There is a predetermined pressure level where the valve would release extra pressure if the latter exceeds the preset level.
- ● Can be used in all types of gas and liquid applications.
- ● Can also be used in high pressure and temperature applications.
- ● Cost-effective.
- ● The spring mechanism and corrosive material do not blend well.
- ● Back pressure could affect valve functions.
Pressure relief valves are effective when back pressure is not a major consideration. Pressure relief valves can be seen in boiler applications and pressure vessels.
Above are the 9 types of valves used in today’s industrial world. Some act as tight protection against leakage while others are great throttlers. By understanding each valve, learning how to apply them to the industry becomes much easier.
