1. Manufacturing materials
A valve is applied to various fields because of its variety, and its applications differ greatly. A valve can be used in many working conditions such as high-temperature and high-pressure, low-temperature, flammable and explosive, highly toxic and strong corrosive media, and demanding requirements are put forward. Carbon steel, alloy structural steel, CrNi stainless steel, CrMoAl nitrided steel, CrMoV heat-resistant steel, CrMnN acid-resistant steel, precipitation hardening steel, duplex stainless steel, low-temperature steel, titanium alloy, and Monel are also adopted often besides cast iron. It's difficult to process these materials containing many alloys due to their poor casting, welding and processing. Moreover, these materials are valuable materials which have high alloy content, good strength and hardness, so we will encounter many difficulties in material selection, material preparation, and procurement. For some materials, they are not easy to be purchased because they are not used often.
2. The structure of the casting
Complicated thin castings are adopted for most castings. They are required to have not only a good appearance but also compact internal quality and good metallographic structure. Defects such as gas holes, shrinkage cavities, sand inclusion and cracks are not allowed, resulting in a complicated casting process and difficult heat treatment. The pressure-bearing thin castings are much more difficult and complicated than the other mechanical component castings in the machinery industry.
3. Machining processes
Most materials with good strength, good hardness and high corrosion resistance have poor cutting performance. The required dimensional accuracy and smoothness are difficult to obtain and there is a certain difficulty for the machining tools, processes and equipment. For example, stainless steel and acid resistant steel containing high alloy content have the disadvantages of good toughness, good strength, poor heat dissipation, great chip viscosity, and good work hardening tendency. Moreover, there are high requirements on machining accuracy, matching angles, smoothness and matching of seal pairs of sealing surfaces. All these make the processing of the valve more difficult.
4. Process arrangement of valve parts
A valve doesn't have a lot of components and has simple structure. The machining accuracy of most valves is not high, resulting in a rough appearance, which gives the impression of a simple device. Actually, the heart of the valve is extremely precise. There are very high requirements on the flatness, hardness and smoothness of the sealing surface. The degree of the sealing pair composed of two sealing surfaces must reach zero to meet the requirement of no leakage. The most difficult processing is the standard of roughness to ensure the accuracy of the valve's heart.
5. Test and inspection of valves
A valve is an important part for opening, closing and regulating pressure pipelines, and the pressure pipeline has very different working conditions, such as high-temperature and high-pressure, cryogenic, flammable and explosive, highly toxic and strong corrosion conditions. However, the test and inspection conditions of valve manufacturing cannot meet the same requirements as the working conditions. Various international and domestic valve test standards stipulate that the test is performed under conditions close to normal temperature, using gas or water as the medium. There will be a fundamental hidden danger, that is, a valve which is qualified after the factory test can't meet the use requirements due to material selection, casting quality and damage of sealing under harsh actual conditions. Major accidents may even occur due to quality.
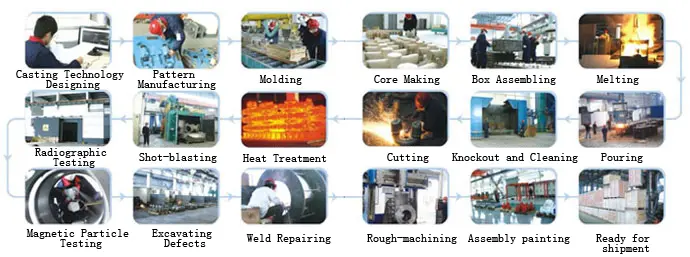
The manufacturing processes of valves
The manufacturing processes of valves are as follows: The manufacturing of valve bodies, valve’s inner parts such as valve seats, valves stems and valve discs, manufacturing of fasteners, assembly, inspection and test. The manufacturing of valve bodies includes casting, surfacing, ultrasonic flaw detection according to drawings, surfacing and post-welding heat treatment, fine processing, sealing surface grinding, the hardness inspection of the sealing surface and liquid penetrant tests. The manufacturing of internal parts is as follows: Purchase raw materials based on the standard. Inspect raw materials in the factory. Manufacture the casting by round steel or forgings according to the requirements of drawings. Roughly machine the ultrasonic flaw detection surface if it is required. Roughly machine surfacing grooves. Perform surfacing and post-welding heat treatment. Finely machine all parts. Grind the sealing surface. Test the hardness of the sealing surface and conduct color flaw detection. The manufacturing of the stem includes the procurement of raw materials, inspection in the factory, castings, rough machining of surfacing grooves, surfacing and post-welding heat treatment, fine processing, grinding of the outer part, surface treatment of valve stems such as nitriding, quenching and electroless plating, final treatment (polishing and grinding), grinding of sealing surfaces, hardness inspection of sealing surfaces and liquid penetrant tests. The manufacturing processes of internal parts not requiring surfacing of sealing surfaces are as follows: Purchase raw materials based on the standard. Inspect raw materials in the factory. Manufacture castings by round steel or forgings according to the drawing. Roughly machine the ultrasonic flaw detection surface if it is required. Finely machine various parts. The manufacturing of fasteners should comply with the DL439-1991 standard. Raw materials should be inspected in the factory after they are purchased. Castings should be manufactured based on the drawings and inspected. Perform rough machining and then fine machining. At the end, conduct the spectral inspection.
Assembly and tests of the valve include gathering parts, cleaning of the parts, rough assembly of the parts according to drawings, hydraulic tests, shell tests, upper sealing tests, low-pressure sealing tests, high-pressure sealing tests and high-pressure gas shell tests based on drawings, disassembling and clean the valve after the test, final assembly, testing of the actuator (for electric valves), paint, packaging and shipment.